Does the US Import or export more? A great question that needs to be answered! As the United States, a powerhouse in the global economy, buys and sells goods and services to countries around the world.
To understand the health of its economy and its place in international trade, it’s important to look at the balance between what it imports and what it exports.
This blog post will dive into the details of exports and imports US data. We’ll examine how these have changed over time and discuss the factors that influence them.
Table of Contents
US Import Trends Over the Years
The United States has long been a major importer of goods and services, and this trend has continued over the decades. Several factors have contributed to the growth in US imports:
- Consumer Demand: The increasing purchasing power of American consumers has led to a higher demand for a wide range of products, many of which are imported.
- Manufacturing Outsourcing: US companies have increasingly outsourced manufacturing operations to other countries, often in search of lower labor costs and other economic advantages. This has resulted in a surge in imports of manufactured goods.
- Globalization: The globalization of the world economy has made it easier for US businesses to source products from around the globe. This has led to a more diverse mix of imports, including everything from raw materials to finished goods.
While US imports have generally increased over time, there have also been periods of fluctuation. Economic downturns, trade disputes, and other factors can influence import levels.
For example, the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted global supply chains and led to temporary declines in imports.
Specific Years and Trends for US Import
2000s: The early 2000s saw a significant increase in US imports, driven by economic growth and the outsourcing of manufacturing jobs. China emerged as a major source of imports during this period.
2008-2009: The global financial crisis, known as The Great Recession has led to a temporary decline in US imports as consumer spending and business investment slowed.
2010s: Following the financial crisis, US imports began to rebound, with strong growth in areas such as vehicles, electronics, and consumer goods.
2020-2021: The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted global supply chains and led to temporary shortages of certain imported goods. However, US imports rebounded strongly in 2021 as the economy recovered from the pandemic.
Read more: The Positive and Negative Impacts of the Amazon Effect on Freight in Dubai
US Export Trends Over the Years
The United States has also been a major exporter of goods and services, and its export activities have evolved significantly over time. Several factors have influenced the growth and development of US exports:
- Economic Growth: Periods of economic growth in the United States have often been accompanied by increases in exports as businesses seek to expand their markets and capitalize on global opportunities.
- Technological Advancements: The development of new technologies has enabled US companies to produce high-quality, competitive products that are in demand internationally.
- Trade Agreements: Trade agreements, such as NAFTA and the USMCA, have facilitated US exports by reducing trade barriers and improving market access.
Specific Years and Trends for US Export
1990s: The 1990s saw a significant increase in US exports, driven by economic growth and the implementation of trade agreements such as NAFTA.
2000s: The early 2000s were a period of continued growth in US exports, with strong performance in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and technology.
2008-2009: The global financial crisis led to a temporary decline in US exports as global demand weakened.
2010s: Following the financial crisis, US exports began to rebound, with strong growth in areas such as energy, agriculture, and manufacturing.
2020-2021: The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted global supply chains and led to temporary declines in US exports. However, exports rebounded strongly in 2021 as the economy recovered from the pandemic.

Learn more: Exploring Global Sourcing Advantages and Disadvantages
Factors Influencing exports and imports US Data
Exports and imports US trade is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, both domestic and international. These factors can include:
1- Domestic Factors:
- Economic Conditions: The overall health of the US economy, including GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer confidence, can significantly impact trade patterns.
- Monetary Policy: Interest rate changes by the Federal Reserve can affect the value of the US dollar, which in turn can influence the competitiveness of US exports and imports.
- Government Policies: Trade policies, such as tariffs, can have a direct impact on the cost and competitiveness of US goods and services in international markets.
- Technological Advancements: The development of new technologies can enhance the competitiveness of US exports and create new opportunities for trade.
2- International Factors:
- Global Economic Conditions: The economic health of major trading partners, such as China, and the European Union can influence US trade flows.
- Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates can affect the relative prices of US goods and services in international markets.
- Trade Agreements: Trade agreements can reduce trade barriers and facilitate trade between the United States and its trading partners.
- Geopolitical Events: Political instability, conflicts, and natural disasters in other countries can disrupt global supply chains and impact US trade.
For more info: Mass vs Tailored Logistics – Which is Better in 2024?
Does the US Import or Export More?
The United States imports more than it exports according to the Council on Foreign Relations. This means it has a trade deficit.
While the US is a major exporter of goods and services, it is also the world’s largest importer. This is largely due to its large and diverse economy, which requires a wide range of goods and services that are often produced more efficiently or cheaply elsewhere.
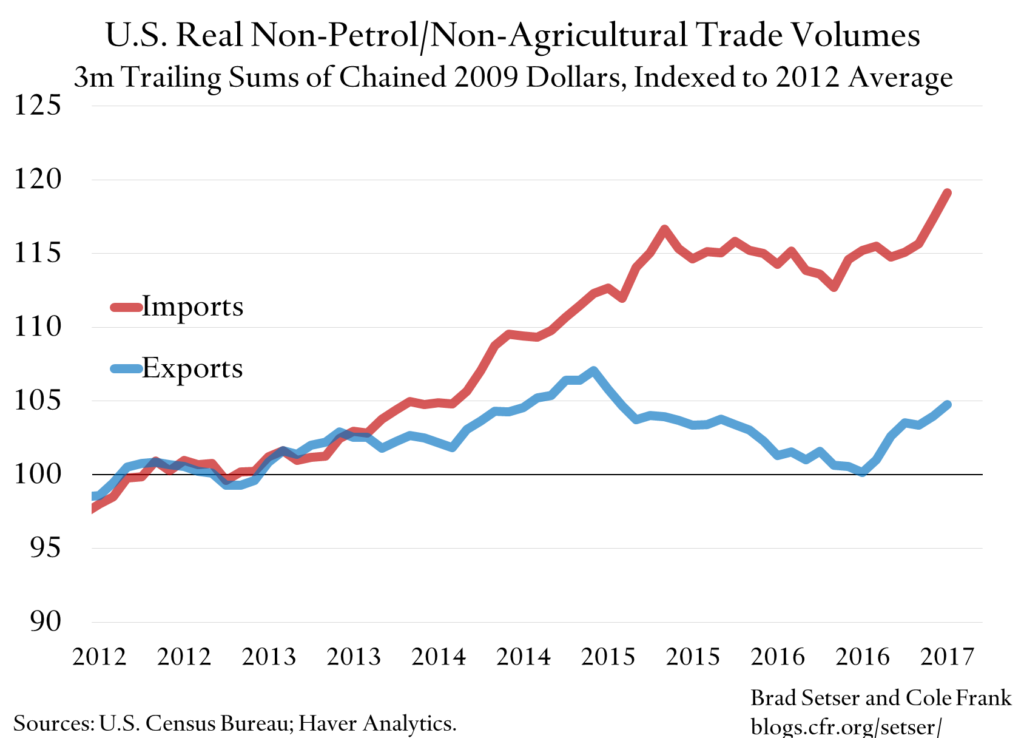
Here are some key factors contributing to the US trade deficit:
- Consumer Demand: Americans have a strong appetite for a wide variety of goods and services, many of which are imported.
- Manufacturing Outsourcing: US companies often outsource manufacturing to countries with lower labor costs.
- Globalization: The connections of the global economy make it easier for US businesses to source products from around the world.
- Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates can affect the relative prices of US goods and services in international markets.
Learn more: Embracing Green Last-mile Delivery in Dubai for 2024
Concluding our thoughts on the exports and imports US
The United States’ trade patterns are complex and constantly changing. Economic conditions, government policies, and world events all play a role.
While the exports and imports US has often bought more than it sold, recent trends suggest it’s working towards a more even balance.
Our experts at Z-Line Logistics Company study the exports and imports US data, so we can gain valuable insights into the nation’s economic health, its relationships with other countries, and its importance in the global economy.
FAQs about exports and imports US
- What are the imports and exports of the United States?
The nation acts as a global trade powerhouse, exchanging machinery, energy, and food with partners worldwide. These exports and imports US activities are the backbone of the economy and satisfy massive consumer demand.
- What are the 5 biggest exports for the US?
Top categories include refined petroleum, aircraft parts, crude oil, natural gas, and advanced electrical machinery. These sectors define the exports and imports US landscape, bringing in billions from global trade partners.
- What are the top 5 imports in the US?
Consumer needs drive the high intake of cars, crude oil, computers, broadcasting equipment, and life-saving medications. Analyzing these exports and imports US trends shows a strong reliance on international manufacturing for tech and health.
- Is the US the largest importer or exporter?
The U.S. is currently the world’s top importer and the second-largest exporter, trailing only behind China. This specific balance is a primary driver of modern exports and imports US economic policy and trade negotiations.




